Installing openCARP
The openCARP ecosystem comprises the openCARP simulator, carputils, meshtool, meshalyzer, LimpetGUI, carputilsGUI and a number of examples as detailed here. Here, we provide instructions for:
- Installing openCARP, optionally with carputils and meshtool (see the next section)
- Installing meshalyzer
- Installing LimpetGUI (Instructions available in the code repository)
- Installing carputilsGUI
How to install openCARP
In this section, we provide instructions for installing the openCARP simulator, the carputils framework and meshtool. If you do not wish to develop in openCARP, we advise you to install all three together, using one of the methods provided below:
- Precompiled installation packages for Linux and macOS
- Docker containers
- Building from sources
- Spack package
If you don't know which method to choose, you can refer to the following decision tree.
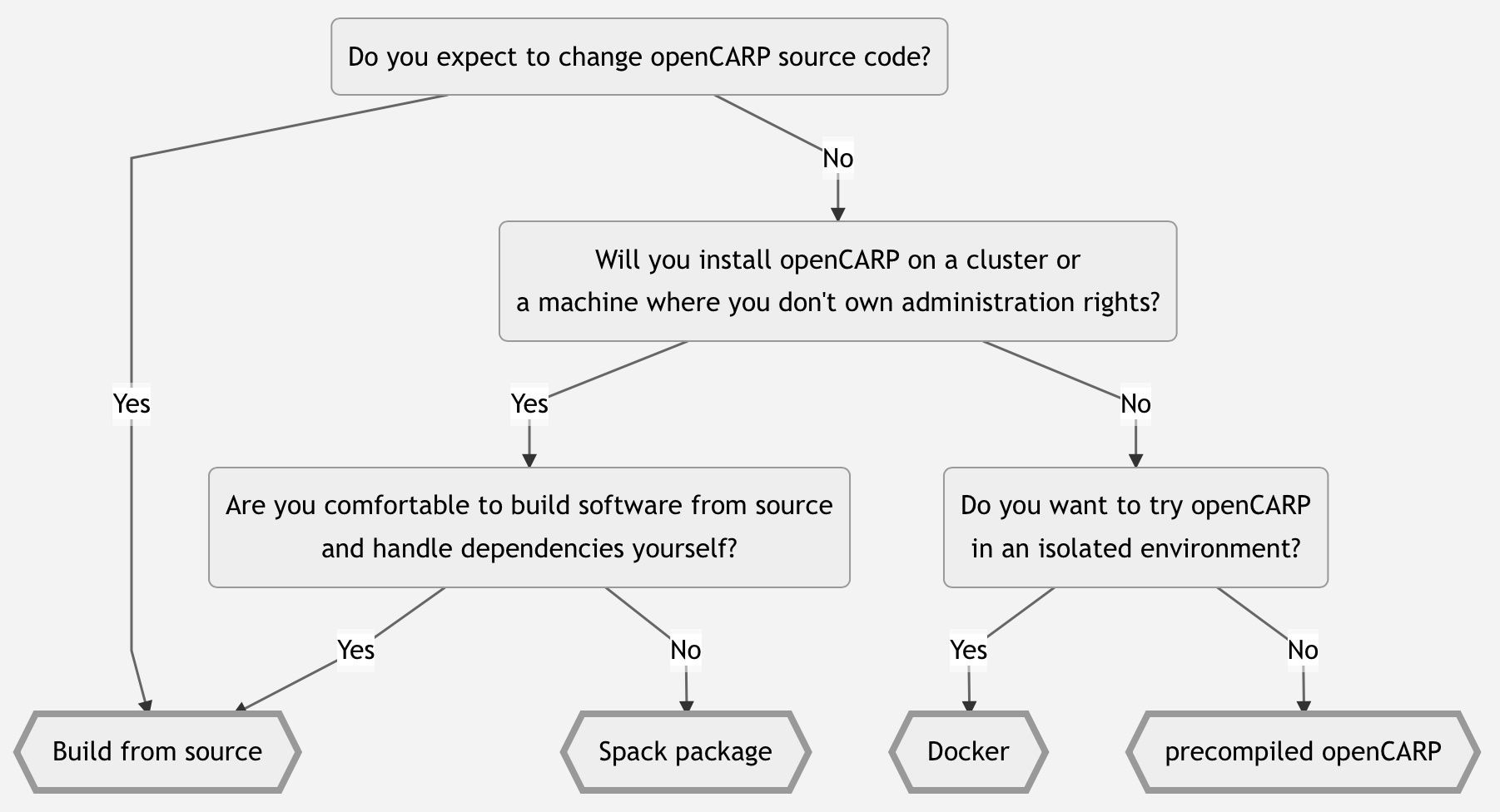
If you installed openCARP without carputils, you can also find the instructions for installing carputils alone.
Note for Windows users: you can try openCARP on Windows by using the Docker containers. If you use Windows 10 or Windows 11, you can also consider using the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) and following the Linux installation instructions.
Installation of Precompiled openCARP
Before installing openCARP, install Python3 and pip.
Using your package manager would be preferable for most users.
Make sure they work by running the following commands.
python3 --version
python3 -m pip --versionFor Ubuntu users: you might require to run these commands before installing your python3-pip.
add-apt-repository universe
apt-get update1. Installation Packages
We provide openCARP installation packages on our release page. Currently, they will install openCARP, carputils, meshtool, and the examples. Meshalyzer is not yet included, please install it separately.
After installation, you can find the examples installed to /usr/local/lib/opencarp/share/examples.
Linux
DEB package (Ubuntu and Debian)
For Ubuntu and Debian, please download the .deb package.
Note: the packages of versions <= 9.0 are compatible with Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04, and Debian 10 (and potentially more recent distributions). The packages of openCARP versions from 10.0 to 17.0 are compatible with Ubuntu 20.04 and 22.04, and Debian 11 (and potentially more recent distributions). openCARP versions > 17.0 provide a package compatible with Ubuntu 22.04, 24.04 and Debian 12, as well as a package compatible with Ubuntu 20.04 and Debian 11. If the latest
.debpackage is not compatible with your OS version, we invite you to use the AppImage package.
Installing the package can require to install the following packages as a prerequisite:
apt-get install git python3 python3-testresources python-is-python3We recommand to install the package via apt-get like
cd <path-to-your-downloaded-deb-file>
apt-get update
apt-get install ./opencarp-vXX.X.debwith XX.X the version that you downloaded.
RPM package (RHEL, Rocky Linux, CentOS, Fedora)
For RHEL, Rocky Linux, CentOS (8 or later) or Fedora (31 or later), please download the .rpm package.
We recommand to install the package via dnf like
cd <path-to-your-downloaded-rpm-file>
dnf install ./opencarp-vXX.X.rpmwith XX.X the version that you downloaded.
Alternative if precompiled packages don't work for you: the AppImage package
If the above packages don't work for you for some reason (no support of the operating system, no superuser permissions, etc.), please use the openCARP AppImage, which is a package for any recent enough Linux-based operating system. The documentation for using the AppImage is available inside the README.md file of the AppImage package or here.
The AppImage only supports openCARP binaries, meshtool and carputils installation, so please check other components (examples and Meshalyzer) according to your needs.
Note: If you are not using carputils, and want to run simulations with MPI using a command such as
mpiexec -n 4 openCARP ..., you will in addition have to add the location of the MPI executables to your path by running the command:export PATH=/usr/local/lib/opencarp/lib/petsc/bin:${PATH}.
To finish the installation, you should now set up carputils
macOS
For macOS (10.14 or later), please download the .pkg installer. Before running the installer, call xcode-select --install on the command line (Programs -> Utilities -> Terminal).
Note: For versions of openCARP >11.0, please use the
.pkginstaller coresponding to the architecture of your computer: use thearm64installer for an Apple Silicon computer, and thex86_64installer for systems with an Intel chip. If you don't know which one to choose, click on the Apple logo on the top left of the screen, then click on "About This Mac". If your processor's name contains "Intel", then use thex86_64installer ; if it contains "Apple", use thearm64installer.
You may need to open the installer using the context menu (right click on the item and then select Open) to confirm the security warning.
To finish the installation, you should now set up carputils
Note: If you are not using carputils, and want to run simulations with MPI using a command such as
mpiexec -n 4 openCARP ..., you will in addition have to add the location of the MPI executables to your path:export PATH=/usr/local/lib/opencarp/lib/openmpi/bin:${PATH}
2. Set up carputils
If you want to use openCARP with carputils, you should also set up carputils. With the command install_carputils.sh, you can create a virtual environment containing carputils in the current directory:
install_carputils.shYou can then activate this environment and start using carputils:
. ./venv_carputils/bin/activateTo check that carputils has been set up correctly, you can run the command cusummary, which will give you some information about the carputils settings.
You can deactivate carputils environment at any time with the command deactivate.
Note: carputils' environment will only be activated for your current session. In particular, it must be activated again if you want to use carputils in a new terminal window.
Note: alternative ways for installing carputils are available in the carputils installation section.
3. Confirm the Installation
To confirm if the package is successfully installed, open a terminal and try the following commands.
Run openCARP binary as follows. If it prints the building information (e.g. GITtag: v10.0, etc), your openCARP is successfully installed. Enjoy the simulator!
openCARP -buildinfoRun carputils in Python as follows. If it prints the installation location, your carputils is successfully installed. Enjoy Python coding!
python3 -c "import carputils; print(carputils)"Docker
If you want to keep your host system clean but still be able to run and change openCARP, our Docker container might be most suitable for you. Docker containers should also run on Windows. See docker/INSTALL.md for detailed instructions on how to install and use (docker/README.md) the openCARP docker container.
Installation from Source
If you expect to change the openCARP source code, we suggest you follow the build instructions (docs/BUILD.md) to install from source.
Installation of openCARP Docker containers
First, install Docker for your platform.
There are 2 options for the openCARP installation using Docker.
- After the Docker installation use docker commands to pull and use the docker images.
- Alternatively, install using our script which will take care of all installation steps for you.
Pull the docker image (Option 1)
Pull the latest openCARP docker image:
docker pull docker.opencarp.org/opencarp/opencarp:latestRun the docker image using the following terminal command:
docker run -it docker.opencarp.org/opencarp/opencarp:latestYou can now use openCARP. To get started, go to the directory containing the examples:
cd /openCARP/examplesand head over to the examples section.
NOTE: You can share a directory between your host machine and the docker container by running the container with the following command:
docker run -it -v /path/in/your/machine:/path/in/container docker.opencarp.org/opencarp/opencarp
For usage examples and more information, please refer to our docker/README.
Install our docker script (Option 2)
Docker provides a variety of commands to utilize docker images:
docker --helpTo help you quick start, our script wraps the most commonly used docker commands.
Tell the install script where to place the binary files (should be a diretory in your $PATH). Use sudo if admin permission is required to write there:
cd <path-to-your-codebase>/openCARP/docker
./install_script.sh <path-to-your-bin>For example, to install to /usr/local/bin, run:
sudo ./install_script.sh /usr/local/binThe script enables you to start with the keyword opencarp-docker followed by the appropriate command.
Make sure the script is installed correctly:
opencarp-docker helpPull the docker image:
opencarp-docker pullFor usage examples and more information, please refer to our docker/README.
Visualization
For visualization, please refer to installation of meshalyzer and locally install meshalyzer because it is not included in the Docker container.
Building from Source
After making sure the prerequisites are installed, you can build openCARP using CMake (recommended) or the shipped Makefile.
Prerequisites
First install the following openCARP prerequisites using your package manager (e.g. apt or rpm on Linux, homebrew or macports on macOS) or from source.
- binutils
- C and C++ compilers (e.g. gcc/g++ or clang/clang++. On macOS, we recommend clang provided by the homebrew package llvm to support openMP)
- CMake (Optional, minimum required version 3.13)
- FFTW3 (Optional, for building
igbdft) - gengetopt (mininum version for current compilers: 2.23)
- gfortran
- git
- make
- PETSc
- PkgConfig
- Python3 and the pip package installer
- SUNDIALS (Optional, for using advanced ODE time integration)
- zlib development package
Building PETSc from source would be a better practice, so you could configure it depending on your needs.
If you are not experienced with its various configurations, please refer to the following suggestions.
Set --prefix= to the location you would install PETSc.
After installation, set the environment variable PETSC_DIR and PETSC_ARCH accordingly.
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/petsc \
--download-mpich \
--download-fblaslapack \
--download-metis \
--download-parmetis \
--download-hypre \
--with-debugging=0 \
COPTFLAGS='-O2' \
CXXOPTFLAGS='-O2' \
FOPTFLAGS='-O2'
make all
make installIn this case, to make mpirun available on your machine, add $PETSC_DIR/bin to your PATH. That is, add the following line to your .bashrc (or equivalent if you don't use the bash shell).
export PATH=$PATH:$PETSC_DIR/binIf you have all the listed dependencies, a quick way to get openCARP up and running is the following:
Clone the repository and enter the codebase folder openCARP
git clone https://git.opencarp.org/openCARP/openCARP.git
cd openCARPTo have a more stable environment, we recommend using the latest release version instead of the bleeding edge commit on the master branch:
git checkout latestIf you want to develop and push your changes back to the openCARP repository, then staying on a branch is the better option and you should skip the command above.
We provide CMake files and Makefiles for building the codebase, choose one fits your workflow.
Building using CMake
Use CMake to create the _build build folder, optionally add -DDLOPEN=ON to enable ionic shared library loading, and -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release to optimize compilation.
By default, the OpenMP parallelization is activated for igbutils and meshtool. This is equivalent to setting the option -DUSE_OPENMP=UTILS and requires that OpenMP is installed on your system.
You can use -DUSE_OPENMP=ON to activate OpenMP parallelization globally.
If you want to deactivate OpenMP parallelization completely, set -DUSE_OPENMP=OFF.
If you want to add support for the Caliper performance instrumentation and profiling library,
set -DENABLE_CALIPER=on when running CMake. You can provide a hint to the Caliper installation
directory by setting -Dcaliper_DIR=/your/path. When running the code, set the CALI_CONFIG
variable as shown here: Caliper Region profiling. CUDA profiling with CUPTI is also enabled automatically, but only if Caliper is built with -DWITH_CUPTI=on.
If you also want to build the additional tools (meshtool, carputils, and examples) locally, use in addition the option -DBUILD_EXTERNAL=ON:
cmake -S. -B_build -DDLOPEN=ON -DBUILD_EXTERNAL=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ReleaseIf you do not want to install the additional tools, you can use:
cmake -S. -B_build -DDLOPEN=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ReleaseCompile the codebase, and all built executables will be located in the _build/bin folder.
cmake --build _buildIf you built the additional tools, meshtool executable is also located in the _build/bin folder, carputils and experiments (contain examples) are cloned to the external folder.
The next step is to set up carputils: see the installation instruction for carputils .
Building using the Makefile
The codebase can be compiled using
make setupThis target includes updating the codebase (make update) and code compilation (make all).
Make sure to edit the my_switches.def file to match you requirements (e.g., to enable the use of shared libraries for ionic models).
Links to all compiled executables are located in the bin folder.
Please also refer to the carputils main page, the meshtool main page.
Download the openCARP examples to the location of your choice using git clone https://git.opencarp.org/openCARP/experiments.git.
Installation with Spack
Spack is a package manager for supercomputers, Linux and MacOS. It is designed to make the installation of scientific software easier.
Setting up Spack
To get Spack, clone its repository by entering the following commands in your terminal:
git clone https://github.com/spack/spack.git
cd spackThen set up your environment by sourcing the Spack setup script:
. ./share/spack/setup-env.shIf you are using another shell as bash/zsh/sh, please refer to the Spack documentation to get the appropriate command
Please also note that Spack has some minimum system requirements, which are assumed to be present on the machine where Spack is run.
You can now use the Spack commands.
Install the openCARP Spack package
In order to install openCARP with carputils and meshtool, you can use the following command in the shell:
spack install opencarp +carputils +meshtoolIf the compilers you wish to use are loaded from a module (typical situation on clusters), it is likely that you have to do a modification in the Spack configuration in order to be able to install packages: open the file located at $HOME/.spack/packages.yaml and add the name of the module in the modules field of your compiler. Example of a resulting file:
compilers:
- compiler:
spec: gcc@10.2.0
paths:
cc: /opt/bwhpc/common/compiler/gnu/10.2.0/bin/gcc
cxx: /opt/bwhpc/common/compiler/gnu/10.2.0/bin/g++
f77: /opt/bwhpc/common/compiler/gnu/10.2.0/bin/gfortran
fc: /opt/bwhpc/common/compiler/gnu/10.2.0/bin/gfortran
flags: {}
operating_system: rhel8
target: x86_64
modules: [compiler/gnu/10.2]Using openCARP
Once openCARP is installed, you can load it as it would be done for a module:
spack load opencarpopenCARP is now installed and ready to be used.
Using external packages with Spack
By default, Spack installs all the openCARP dependencies, even if some of them are already installed on the user's system. In order to use external packages in Spack, you can use one of two ways:
- Rely on the
spack externalcommand, e.g.,spack external find cmake. Ifcmakeis found, it will be added to the list of external packages that can be used by Spack. - Modify
~/.spack/packages.yamlor$SPACK/etc/spack/packages.yamlas in the following example:packages: openmpi: externals: - spec: "openmpi@1.4.3%gcc@4.4.7 arch=linux-debian7-x86_64" prefix: /opt/openmpi-1.4.3 - spec: "openmpi@1.4.3%gcc@4.4.7 arch=linux-debian7-x86_64+debug" prefix: /opt/openmpi-1.4.3-debug cmake: externals: - spec: cmake@3.7.2 modules: - CMake/3.7.2 buildable: False
For more information about Spack, see the documentation.
Installing carputils
To locally run carputils on Linux or macOS, first install Python3, pip, and openCARP.
Download carputils
If you have built openCARP with additional tools using CMake, then carputils is available in openCARP/external/carputils.
If you have installed openCARP using the precompiled packages, then carputils is available in /usr/local/lib/opencarp/share/carputils.
Otherwise, clone the carputils repository and enter the codebase folder carputils.
git clone https://git.opencarp.org/openCARP/carputils.git
cd carputilsInstallation
This section explains how to build carputils and install it using pip.
This is recommended if you do not expect to develop carputils.
In order to avoid conflicts in Python dependencies, we recommend to install carputils within a virtual environment. A virtual environment can be created in the current directory with the following command:
python3 -m venv carputils_envThis environment should then be activated each time you want to use carputils with:
. ./carputils_env/bin/activateOnce the environment is activated, install carputils with pip:
python -m pip install /path/to/carputilswhere /path/to/carputils should be replaced with the path to the carputils folder.
You can then generate the carputils settings file settings.yaml if it does not exist:
cusettings $HOME/.config/carputils/settings.yamlThis file contains the carputils settings, including the paths to openCARP binary files. It contains default values adapted to your local setup, but can be modified manually.
Note: if the directory containing the openCARP binary files is not in your PATH (most likely if you compiled openCARP from sources), you will have to change the default value of
CARP_EXE_DIRin the settings file. For example, if youropenCARPexecutables are located at/home/openCARP/_build/bin, you will have to edit the file and setCARP_EXE_DIRtoCARP_EXE_DIR: CPU: /home/openCARP/_build/bin
On the other hand, if you plan to develop carputils, manually configuring it as follows is recommended.
Alternative: development installation
Enter the carputils directory and follow the instructions to do a development installation of carputils.
Install the dependencies using pip - preferably into user-space:
python3 -m pip install --user -r requirements.txtAdd carputils/bin to your PATH, and carputils to your PYTHONPATH.
For example, if carputils is located at $HOME/openCARP/external, add the following lines in your .bashrc:
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/openCARP/external/carputils/bin
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:$HOME/openCARP/external/carputilsCreate a settings.yaml file, which is a summary of paths and (default)
parameters associated with your installation. To generate a default file, run the
following command in the root folder of your carputils installation:
python3 ./bin/cusettings $HOME/.config/carputils/settings.yamlOpen the file and specify the proper directories for openCARP binary files.
Notice using the 2 or 4 characters indentation before the keyword CPU.
CARP_EXE_DIR:
CPU: $HOME/install/openCARP/binSet directories for other openCARP tools if you use them. For example,
MESHALYZER_DIR: $HOME/install/meshalyzerCompiling C extensions and auto-generate code
To compile the C extensions for reading and writing meshes, just call
make
in the root folder of your carputils installation. If carputils is not installed under openCARP/external/carputils, you will also have to provide the path to the openCARP sources root folder:
make OPENCARP_PATH=/path/to/openCARPsourcesIf you need to use a non-default compiler (e.g. under macOS for OpenMP support), provide it as a variable
CC=clang makeA plain make will also auto-generate the model.ionic, model.activetension and model.mechanics
python modules. They can be re-generated manually by calling
make modelsTroubleshooting
The installation of some dependencies of carputils can fail if pip and setuptools are not up-to-date.
They can be upgraded with the following commands:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
python3 -m pip install --upgrade setuptoolsInstallation of meshalyzer
Meshalyzer is regularly used on Linux and Mac machines, and runs under Windows as well.
Binary packages
We provide binary packages on the release page.
Currently, it includes AppImage, which works on any recent enough Linux-based operating system and a .zip
file with a Windows executable.
AppImage (Linux)
- Download the
.AppImagefile of the latest version - Make it executable, for example,
chmod +x Meshalyzer-3.2-x86_64.AppImage - Run it
./Meshalyzer-3.2-x86_64.AppImage
Windows
- Download the
.zipfile of the latest version - Extract it into a folder
- Run
meshalyzer.exe. To access the files on your driveC:\, use the path/cygdrive/cin meshalyzer's file browser.
If you want to build meshalyzer yourself, please check the following sections.
Prerequisities
-
OpenMP is recommended to improve certain operations. For all compilers, except clang supplied by Apple, it is standard. A simple way to include it on Apple machines is with homebrew:
brew install libomp -
FLTK 1.3.x or higher.
-
freetype to render fonts.
-
cmake version 3.12 or higher, if you want to make compiling easier.
-
To make the "windowless" rendering version, OSMesa
-
To read in VTK/VTU format meshes, install VTK development files
-
HDF5 if you want to optionally use HDF5 data containers
Using your package manager is recommended for installing these packages if possible. On macOS, homebrew works for us.
Compiling
Clone the repository and enter the codebase folder meshalyzer.
git clone https://git.opencarp.org/openCARP/meshalyzer.git
cd meshalyzerWe recommend to always use the latest release version as the master branch is continuously under development and might not be as robust as the releases:
git describe --tags --abbrev=0 returns the latest release version (e.g. '2.2'). Then you can check out this version:
git checkout 2.2.
We provide Makefiles and CMake files for compiling the code, choose the one that fits your workflow.
Makefile
-
Edit make.conf, to set the following:
-
If VTK is installed, set the
VTK_INCandVTK_DIRvariables to point to the directories containing the VTK header files and libraries, respectively. Comment them out otherwise. -
If you have an Apple machine, make sure that HAVE_RETINA is correct.
-
If rendering is really slow and you have an AMD graphics card, uncomment AMD_VIDEO.
-
To use glfw instead of glut, set GLUT_ON to 0.
-
If you want to use the HDF5 data format, uncomment
HDF5=1
-
-
Type
make -j -
For the windowless version, type
make mesalyzer -
The compiled executables will be found in the directory.
-
Copy the binaries to a suitable location
CMake
-
We suggest to run CMake by out-of-source builds, which means all the compiled code goes into a
_builddirectory separate from the source code. -
If VTK is installed, type
cmake -S. -B_build. Otherwise typecmake -S. -B_build -DUSE_VTK=OFF -
Compile the code via
cmake --build _build -
In the main meshalyzer directory, you will find a link to the compiled executalbe.
ccmake
For those who are familiar with ccmake:
-
ccmake . -
configure, edit and generate
-
make -j
Documentation
To compile the manual (LaTeX required)
cd manualpdflatex manualpdflatex manual
macOS
First of all, the command line tools or Xcode must be installed. Next, install the prerequisities using your package manager. We use homebrew as an example.
brew install libpng
brew install fltk
brew install freetype
brew install git
brew install cmakeFollow the steps in the Compiling to build the code.
Linux
For installing meshalyzer first you need to install the "Prerequisites" using your package manager (e.g. apt, yum, or dnf).
The Dockerfile provides an installation example based on CentOS7.
Ubuntu
On Ubuntu (tested with Ubuntu 20.04), you can use:
apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
build-essential \
git \
ca-certificates \
fluid \
freeglut3-dev \
libfltk1.3-dev \
libfreetype6 \
libfreetype-dev \
libglu1-mesa-dev \
libpng-dev \
libjpeg-dev \
cmakeFollow the steps in Compiling to build the code.
CentOS
On CentOS (tested with CentOS 7), you can use:
yum update && yum install git \
gcc gcc-c++ \
libpng-devel \
libjpeg-devel \
fltk-devel \
fltk-fluid \
freetype \
freetype-devel \
freeglut-develIf you want to compile meshalyzer with cmake, you will also need cmake version 3.12 or higher.
You can know which version is provided by the package manager with the command:
yum info cmakeIf the version is higher than 3.12, then use:
yum install cmakeOtherwise you can get cmake3 from EPEL. On CentOS 7, you can use:
yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
yum install cmake3Please note that you will then have to use the cmake3 command instead of the cmake command to compile meshalyzer.
You can now follow the steps in Compiling to build the code.
Windows
meshalyzer can be compiled to use the native windowing system under Cygwin.
Cygwin
First, install Cygwin and include the gcc compiler suite along with it. You will need to install at least the following packages:
- gcc-core
- gcc-g++
- cmake
- make
- colorgcc
- libgcc1
- libfreetype
- libfreetype-devel
- libuuid1
- libjpeg8
- libjpeg-devel
- libpng-devel
- libglut3
- libglut-devel
- libGL-devel
- libGL1
- libGLU1
- libGLU-devel
- zlib
- zlib-devel
Make sure libuuid-devel is NOT installed. Remove it if need be and be warned, it can be persistent.
To pre-select the packages during installation just run
setup-x86_64.exe -P gcc-core gcc-g++ make libgcc1 colorgcc libuuid1 libjpeg8 libjpeg-devel libpng-devel libglut3 libglut-devel zlib zlib-devel libGL-devel libGL1 libGLU1 libGLU-devel
from the Windows commandline.
FLTK
Do NOT use the Cygwin FLTK package. Download the source, and then open a Cygwin terminal. Unpack the source, cd to the top-level FLTK directory and execute. We use version 1.4.4 currently.
./configure --enable-cygwin
make -j
make installIf there is an error compiling fluid, change all ocurrences of_snprintf to snprintf in
fluid/ExternalCodeEditor_WIN32.cxx
To compile meshalyzer, clone it, cd to the top-level source directory
make -jPost-compilation
You can execute meshalyzer by typing ./meshalyzer
See README.md for an example.
To make meshalyzer available from anywhere on your machine, you need to copy it to your bin directory, or add the meshalyzer directory to PATH by editing your .bashrc (or .bash_profile). Using the nano editor as an example, type the following command into the terminal:
nano ~/.bashrcThis will open an editor, scroll all the way down and add the following line, replacing '/home/somefolder/anotherfolder/meshalyzer' with the path of your meshalyzer folder:
export PATH=$PATH:/home/somefolder/anotherfolder/meshalyzerpress Control+X, then type Y and Enter to save the changes. Close all terminal instances!
open a terminal and type meshalyzer
Recent questions tagged installation-containers-packages, petsc, mpi, compilation, docker, spack, carputils, meshalyzer, macos, windows, hpc, cpu
There are tagged with installation-containers-packages, petsc, mpi, compilation, docker, spack, carputils, meshalyzer, macos, windows, hpc, cpu.
Here we display the 5 most recent questions. You can click on each tag to show all questions for this tag.
You can also ask a new question.
